Off-site construction in high-rise residential: Insights from BDP Quadrangle
Author: OCRC
Posted on Mar 7, 2025
Category: Off-site Construction
The construction industry is facing increasing pressure to address housing affordability, labor shortages, and sustainability goals. Off-site construction (OSC) is emerging as a critical solution to these challenges, offering efficiency, cost certainty, and improved quality control. BDP Quadrangle, a leading architecture and design firm, is at the forefront of integrating OSC into high-rise residential projects.
During a recent webinar, Michelle Xuereb, Director of Innovation at BDP Quadrangle, shared key insights into how OSC can transform urban housing projects, the challenges and opportunities in adopting modular solutions, and real-world case studies that highlight the impact of off-site construction.
Why off-site construction?
OSC offers a range of benefits that make it particularly well-suited for high-rise residential buildings. Some of the key drivers for OSC adoption include:
- Affordability and housing crisis: With skyrocketing housing demand and construction costs, OSC enables faster delivery of housing units at a more predictable cost.
- Sustainability and carbon reduction: Prefabrication methods reduce material waste, optimize energy usage, and minimize site disturbances.
- Supply chain volatility: By shifting more of the construction process to a controlled factory setting, OSC mitigates supply chain risks and labor shortages.
- Design for manufacture and assembly (DfMA): OSC leverages standardized, modular components that improve efficiency, repeatability, and ease of installation.
BDP Quadrangle emphasizes that early collaboration and careful planning are crucial for the successful adoption of OSC in high-rise projects.
Understanding the taxonomy of off-site construction (OSC)
The framework for Off-Site Construction (OSC) is built upon Design for Manufacture and Assembly (DfMA), which serves as the overriding philosophy guiding the optimization of construction processes. DfMA emphasizes principles such as standardization, modularity, ease of assembly, and minimizing handling and transportation, making construction more efficient and cost-effective.
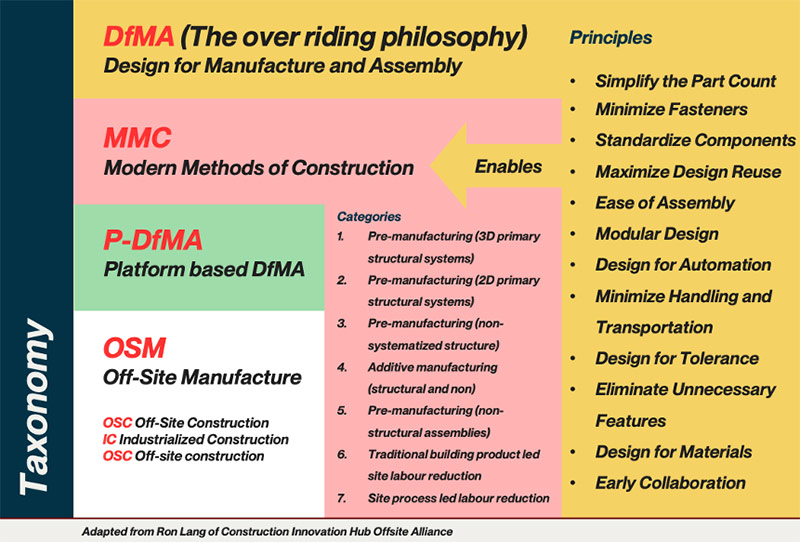
Figure via BDP Quadrangle, adapted from Ron Lang of Construction Innovation Hub Offiste Alliance
Under this philosophy, Modern Methods of Construction (MMC) enable innovative construction techniques. These techniques fall into seven key categories, ranging from pre-manufacturing (both 2D and 3D structural systems) to additive manufacturing and traditional site labor reduction.
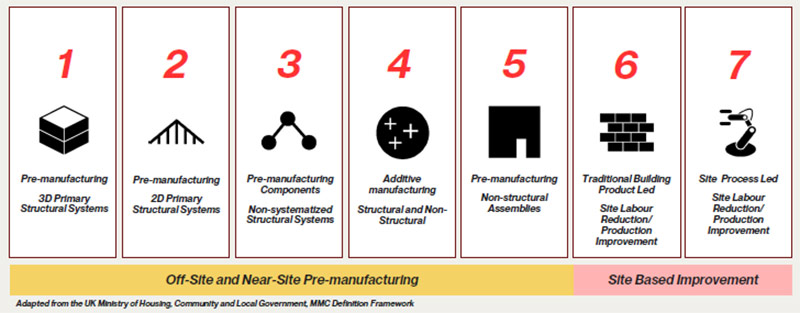
Figure via BDP Quadrangle, adapted from the UK Ministry of Housing, Community and Local Government, MMC Definition Framework
By embracing this structured approach to OSC, the industry can enhance productivity, reduce waste, and create more sustainable, high-quality buildings while addressing labor shortages and supply chain challenges.
The power of concurrent engineering in off-site construction
Concurrent engineering is a transformative approach that streamlines traditional workflows by integrating multiple project stages simultaneously rather than sequentially.
As presented in the diagram by BDP Quadrangle, current coordination within the RIBA stages follows a linear process, where each stage is completed before the next begins. However, concurrent engineering compresses the RIBA stages, allowing different phases to overlap, leading to substantial time savings. By incorporating DfMA (Design for Manufacture and Assembly) workflow integration, specialist contractors and consultants can provide input earlier in the process, enabling faster approvals and reducing delays.
The benefits of this approach include accelerated project timelines, enhanced collaboration, and improved cost efficiency. By leveraging concurrent engineering, the construction industry can move towards a more efficient and integrated delivery model, ultimately improving project outcomes and sustainability.
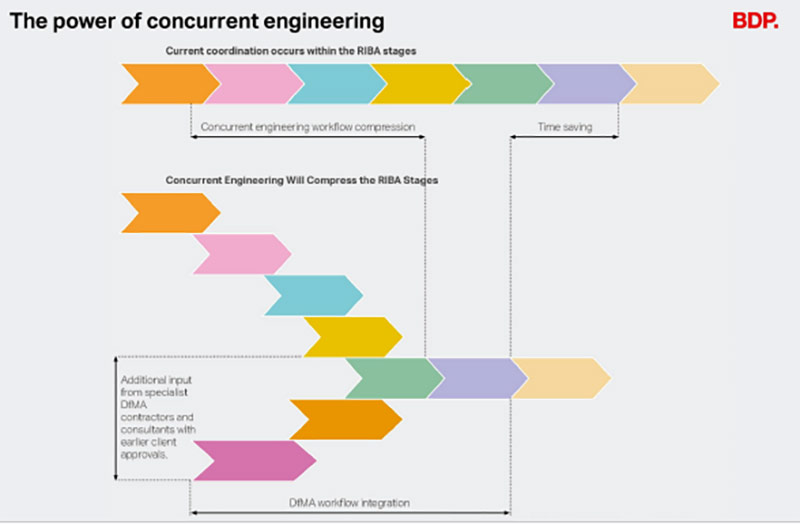
Figure via BDP Quadrangle, adapted from the UK Ministry of Housing, Community and Local Government, MMC Definition Framework
Case studies
Innovative construction methods are transforming how high-rise buildings are designed and built, improving efficiency, reducing on-site labor, and accelerating project timelines. The following case studies highlight real-world applications of precast and modular construction techniques, showcasing their impact on large-scale developments.
From CG Tower in Vaughan, where precast wall panels with pre-installed windows streamlined installation, to Valhalla Village, where an MPS Precast Structural System dramatically reduced on-site workforce requirements, these projects exemplify the benefits of modern construction approaches. Through these examples, we explore how design and construction integration can enhance speed, quality, and sustainability in high-rise developments.
CG Tower, Vaughan Ontario – Precast Wall panels with Windows pre-installed, Global Precast and AWD Windows for the Cortel Group.

Valhallah Village, Block D – MPS Precast Structural System and Precast wall system with State Windows pre-installed for KingSett Capital
- Comparing traditional construction on Tower A with MPS system on Tower D, 70% fewer workers on site. One floor of structure and envelope installed every two weeks

- Design on the left, Construction on the Right
The Future of Off-Site Construction in High-Rise Residential
OSC is poised to play a significant role in the future of high-rise residential construction. As more developers, architects, and builders recognize the benefits, the industry is shifting toward a hybrid model that combines traditional methods with modular and prefabricated solutions.
BDP Quadrangle’s commitment to advancing OSC through research, case studies, and practical implementation is helping to shape the future of high-density urban development.
Did you miss the webinar?
Watch the presentation to learn more about how off-site construction is transforming high-rise residential projects.
Interested in learning more about off-site construction? Join us on the third Thursday of every month for in-depth discussions with industry leaders.
Email offsiteconstruction@unb.ca to be added to our mailing list.